- Home
- About Us
-
Applications
Municipal
 Municipal Wastewater
Municipal water supply
Recycled Water Reuse
Township water supply and drainage
Industrial Park
New pollutant control
Water ecological restoration project
Municipal Wastewater
Municipal water supply
Recycled Water Reuse
Township water supply and drainage
Industrial Park
New pollutant control
Water ecological restoration project
Industry
 Pretreatment of industrial high-difficulty wastewater
Pesticide Industry
API pharmaceuticals
Chemical waste salt purification
Food & Beverage Industry
Pharmaceutical Purified water
Chip Fabrication
Oilfield reinjection water
Industrial zero emissions
Pretreatment of industrial high-difficulty wastewater
Pesticide Industry
API pharmaceuticals
Chemical waste salt purification
Food & Beverage Industry
Pharmaceutical Purified water
Chip Fabrication
Oilfield reinjection water
Industrial zero emissions
Commercial
 Secondary water supply
Pool & Aquarium
High-quality drinking water POE/POU
Aquaculture
Cooling Circulating water
Laboratory applications
Secondary water supply
Pool & Aquarium
High-quality drinking water POE/POU
Aquaculture
Cooling Circulating water
Laboratory applications
UV-AOPs
 Wastewater Biodegradability
Pretreatment of highly toxic industrial wastewater
Chemical active agents
Cyanide
Organic Complexes
Wastewater Biodegradability
Pretreatment of highly toxic industrial wastewater
Chemical active agents
Cyanide
Organic Complexes
Craftsmanship
 UV disinfection
UV photolysis
UV Advanced Oxidation
Reverse Osmosis
Alternative to pasteurization
UV photochemical reaction
Ozone oxidation
UV disinfection
UV photolysis
UV Advanced Oxidation
Reverse Osmosis
Alternative to pasteurization
UV photochemical reaction
Ozone oxidation
Resource Recycling
 waste plastics
Construction waste
Renovation waste
waste plastics
Construction waste
Renovation waste
-
Products
Municipal
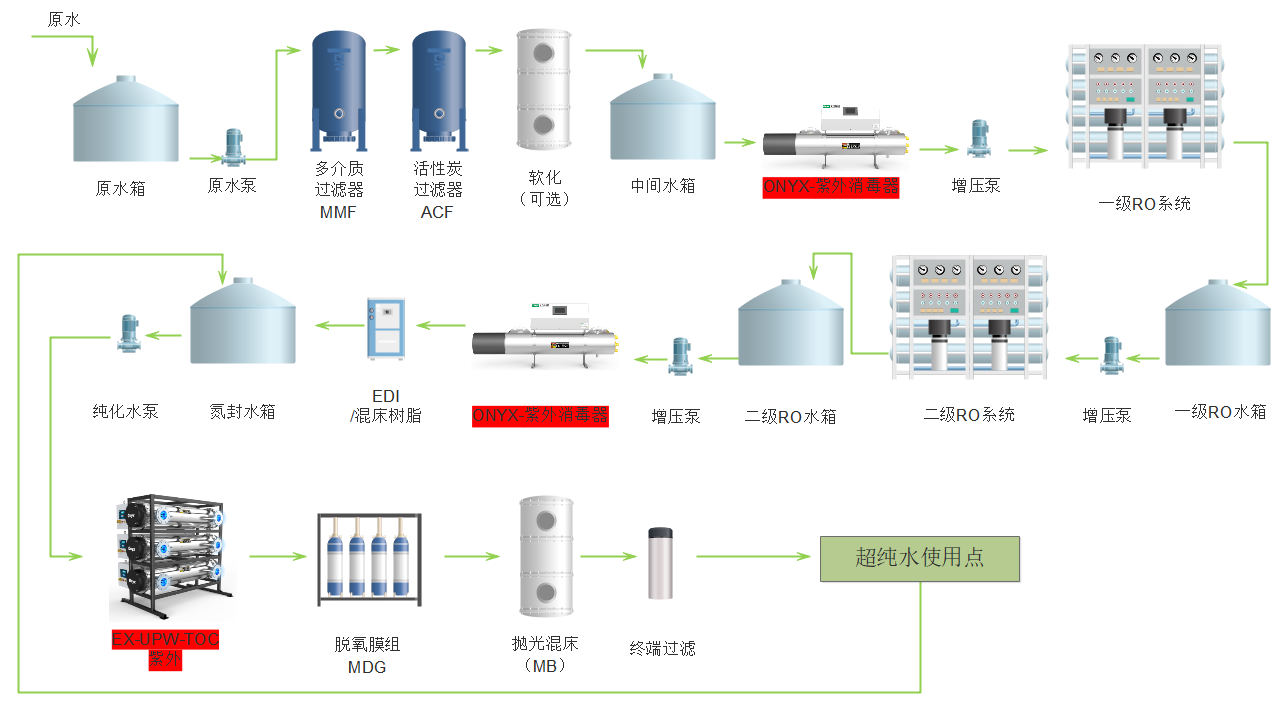
 WSH UV Disinfection System
WTV UV Disinfection Vertical System
ZL UV Disinfection System
Clear Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
MOL Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation System
D.FITE Cloth Filter
WSH UV Disinfection System
WTV UV Disinfection Vertical System
ZL UV Disinfection System
Clear Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
MOL Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation System
D.FITE Cloth Filter
Industry
 ZL UV Disinfection System
Clear Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation
Extrem Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
EX-U UV Sterilizer
EX-UPW-TOC UV TOC System
MOM Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
MOS Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
UV-Fenton
UV-Oxidation
ZL UV Disinfection System
Clear Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation
Extrem Medium Pressure UV Disinfection System
EX-U UV Sterilizer
EX-UPW-TOC UV TOC System
MOM Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
MOS Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
UV-Fenton
UV-Oxidation
Commercial
 EX-L UV Sterilizer
EX-U UV Sterilizer
ZL UV Disinfection System
CLEAR Medium pressure UV Disinfection System
OneUV UV Sterilizer
Extrem Medium pressure UV Disinfection System
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation
MOS Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
COG Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
EX-L UV Sterilizer
EX-U UV Sterilizer
ZL UV Disinfection System
CLEAR Medium pressure UV Disinfection System
OneUV UV Sterilizer
Extrem Medium pressure UV Disinfection System
UV-AOP Advanced Oxidation
MOS Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
COG Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
Photochemistry
 UV-Fenton
Medium-pressure UV-Oxidation
UV Photolysis
Pasteurization UV Alternatives
UV Photocatalysis
Low Pressure UV-Oxidation
UV-Fenton
Medium-pressure UV-Oxidation
UV Photolysis
Pasteurization UV Alternatives
UV Photocatalysis
Low Pressure UV-Oxidation
Resource Recycling
 AI Optical Sorter
Al high-speed sorting robot
AI heavy-duty sorting robot
AI Optical Sorter
Al high-speed sorting robot
AI heavy-duty sorting robot
Others
 SATBR Integrated Wastewater Treatment System
D.FITE Cloth Filter
Modular Wastewater Treatment System
ModuOzone Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
SATBR Integrated Wastewater Treatment System
D.FITE Cloth Filter
Modular Wastewater Treatment System
ModuOzone Ceramic Plate CD Ozone Generator
- News
-
Services
After-Sales Services
 Spare parts replacement
Product Repair
System Support
Renovation
Regular maintenance
Software Upgrade
Spare parts replacement
Product Repair
System Support
Renovation
Regular maintenance
Software Upgrade
Technical Support
 Process Support
Product Training
Research & Development
Small Test
Pilotscale experiment
Online dose monitoring
UV dose design
Process Support
Product Training
Research & Development
Small Test
Pilotscale experiment
Online dose monitoring
UV dose design
Channel Services
 Municipal
Industry
Business
OEM
Municipal
Industry
Business
OEM
Spare parts
 Low Pressure lamps
Low Pressure Amalgam Lamps
Medium Pressure Mercury Lamp
VUV Low-pressure Mercury Lamp(185nm)
Quartz sleeve
Ballasts
UV Intensity Sensor
UV transmittance tester
Sealing accessories
Other
Spare parts replacement
Low Pressure lamps
Low Pressure Amalgam Lamps
Medium Pressure Mercury Lamp
VUV Low-pressure Mercury Lamp(185nm)
Quartz sleeve
Ballasts
UV Intensity Sensor
UV transmittance tester
Sealing accessories
Other
Spare parts replacement
- Resources
- Contact us
- Cn